
SSP’s MIL-DTL-83528 QPL certified EMI shielding silicones meet the requirements of MIL-DTL-83528 and are part of the DLA’s M83528 QPL.
Choose these MIL DTL 83528 gasket materials as sheets, rolls, moldable compounds, extrusions. SSP also makes EMI gaskets in M83528 slash sizes.
SSP’s MIL-DTL-83528 QPL certified EMI shielding silicones meet the requirements of MIL-DTL-83528, a U.S. military specification for electrically conductive elastomeric shielding gaskets. They’re also part of the M83528 Qualified Product List (QPL) from the Defense Logistic Agency (DLA). Our MIL-DTL-83528 Type A, B, C, D, and K elastomers provide offsets to Parker Chomerics CHO-SEAL® materials.

CHO-SEAL 1215 alternative. SSP2569-65 is a 65-durometer, silver-copper EMI shielding silicone. MIL-DTL-83528 Type A. QPL Listed.

CHO-SEAL 1285 alternative. SSP2368-65 is a 65-durometer silver-aluminum EMI shielding silicone. MIL-DTL-83528 Type B. QPL listed.

CHO-SEAL 1217 alternative. SSP2573-75 is a 75-durometer silver-copper EMI shielding fluorosilicone that meets MIL-DTL-83528 Type C. QPL listed.

CHO-SEAL 1287 and CHO-SEAL 1298 alternative. SSP2486-70 is a 70-durometer silver-aluminum EMI shielding fluorosilicone. MIL-DTL-83528 Type D. QPL listed.

CHO-SEAL 1212 alternative. SSP2571-85 is an 85-durometer silver-copper EMI silicone that meets MIL-DTL-83528 Type K. QPL listed.
Military connector gaskets in M83528/004 slash sizes (part numbers)

SSP2486-70 Silver Aluminum Silicone vs. CHO-SEAL 1287 & CHO-SEAL 1298 Data Sheet Outgassing SDS Shielding QPL MIL-DTL-83528 Type D Material SSP2486-70 is a 70-durometer (Shore
Type | Description |
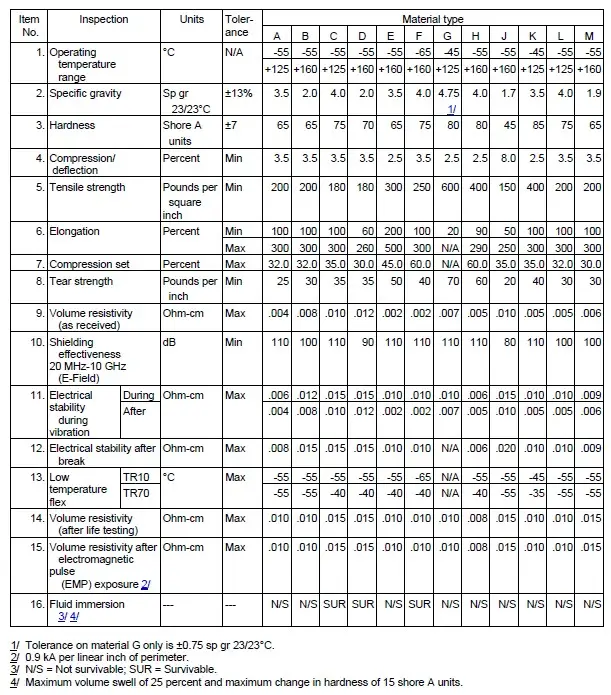
A | Silver-plated, copper-filled silicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +125°C. |
B | Silver-plated, aluminum-filled silicone capable of 100 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +160°C. |
C | Silver-plated, copper-filled fluorosilicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +125°C and resistant to solvents and jet fuels. |
D | Silver-plated, aluminum-filled fluorosilicone capable of 90 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz, with, a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +160°C, and resistant to solvents and jet fuels. |
E | A medium durometer, pure silver-filled silicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +160°C. |
F | Pure silver-filled fluorosilicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with acontinuous use temperature range of -65°C to +160°C and resistant to solvents and jet fuels. |
G | Silver-plated, copper-filled silicone, expanded copper foil reinforced, capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -45°C to +125°C. |
H | A high durometer, pure silver-filled silicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +160°C. |
J | A low durometer, pure silver-filled silicone, capable of 80 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +160°C. |
K | A high durometer silver-plated, copper-filled silicone capable of 110 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous temperature range of -45°C to +125°C. |
L | Silver-plated, nickel-filled silicone capable of 100 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous use temperature range of -55°C to +125°C. |
M | Silver plated glass-filled silicone capable of 100 dB of plane wave shielding effectiveness at 10 GHz with a continuous temperature range of -55°C to +160°C. |
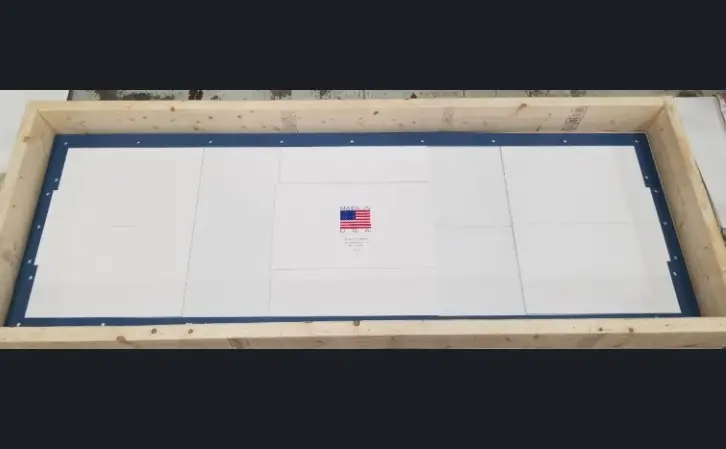

Here at Specialty Silicone Products, we always look for the most efficient way to produce our products. This (above) is a very large silver-aluminum filled fabricated EMI gasket for U.S. Navy use. The material is our SSP2368-65, which meets the full MIL-DTL-83528, Type B requirements. We make this part by bonding several smaller pieces together using conductive adhesive. This process saves hundreds of dollars in costs vs. die cutting from a full sheet.
SSP is QPL listed for this product by the Defense Logistics Agency. These EMI shielding elastomers are considered advanced materials for aerospace, military, and defense and are used to block EMI, EMP, RFI, and RF within avionics, GPS, weapons systems, and other high-end communications equipment and systems.
Filler Material | Base Material | Cost | Max. VR (ohms/cm) | Min. Shielding Effectiveness | Major Advantage or Reason for Use |
Silver-aluminum | Silicone | $$$$ | .008 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Meets MIL-DTL-83528 Type B Offsets Chomerics Choseal 1285 |
Silver-aluminum | Fluorosilicone | $$$$ | .012 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Meets MIL-DTL-83528 Type D |
Silver-copper | Silicone | $$$$ | .004 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Most conductive |
Nickel-aluminum | Silicone | $$$ | .15 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Corrosion resistance |
Nickel-aluminum | Fluorosilicone | $$$ | .25 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Corrosion resistance |
Nickel-graphite | Fluorosilicone | $$ | .1 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Lowest cost fluorosilicone |
Nickel-graphite | Silicone | $ | .1 | 20MHz to 10GHz @ 100dB | Lowest cost silicone |
EMI Military Challenge | Description |
Fixed land-based installations | Electronics at military bases may be near radar systems that produce emissions at levels and frequencies far greater than in commercial settings. Equipment at military facilities may also require protection against an electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generated by high-altitude weapons. |
Mobile land-based installations | EMI threats to technologies used in military vehicles are not unlike the EMI threats faced by conventional vehicles. An EMI military strategy needs to reduce the potential EMI risks associated with exposure to radar and EMP. |
Marine-based vessels | Ships, submarines, and other water-based vessels with metal hulls and superstructures can raise EMI military issues. Devices must be hardened against emissions generated by on-board radio communications and navigation systems. Equipment intended for use below deck may encounter different types of EMI risk than similar equipment used above deck. |
Aviation and aerospace | An EMI military risk that’s unique to aircraft* is potential exposure to high-intensity radio frequencies (HIRF) from radar equipment used by other aircraft operating in proximity during combat. The EMI risk for technologies used in planes, jets, and helicopters depends on whether the equipment is intended to be installed inside or outside of the aircraft. |
*See also “EMI gaskets for avionics help keep military aircraft flying high”, an SSP article in Military Embedded Systems magazine.
SSP also offers these other types of EMII/RFI shielding materials. We also fabricate EMI gaskets and EMI O-rings from the elastomers we make.
MIL‑DTL‑83528 is a U.S. military specification that defines the performance requirements for conductive elastomer EMI/RFI shielding gaskets. It covers electrical conductivity, shielding effectiveness, environmental resistance, compression set, and mechanical durability.
A QPL (Qualified Products List) listing means the material has been independently tested and approved by the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) to meet the exact requirements of MIL‑DTL‑83528. Only materials on the QPL are certified for use in certain military and aerospace programs.
SSP offers multiple QPL‑listed conductive elastomers, including silver‑aluminum and silver‑copper compounds that meet specific MIL‑DTL‑83528 types. These materials are approved for mission‑critical defense and aerospace applications.
SSP manufactures materials that meet several MIL‑DTL‑83528 types, including Type A, Type B, and Type K, depending on the filler system and formulation. Each type defines specific electrical and mechanical performance criteria.
Yes. SSP produces several conductive elastomers that meet or exceed MIL‑DTL‑83528 performance requirements even if they are not QPL‑listed. These materials are often selected for commercial, industrial, or cost‑sensitive applications.
SSP offers compliant materials with silver‑aluminum, silver‑copper, silver‑nickel, and nickel‑graphite fillers. Each filler system provides different levels of conductivity, corrosion resistance, and galvanic compatibility.
Absolutely. SSP supplies MIL‑DTL‑83528‑compliant materials in both silicone and fluorosilicone. Fluorosilicone versions provide added resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents for aerospace and harsh‑environment applications.
These materials are used in military electronics, aerospace platforms, radar systems, avionics, secure communications, and any application requiring proven, certified EMI/RFI shielding performance.
Yes. SSP can provide test reports, QPL certifications, material data sheets, and compliance documentation to support engineering, qualification, and procurement requirements.