RFI vs. EMI: Understanding the Differences
Defining EMI and RFI
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a broad term that refers to the unwanted disturbance caused by electromagnetic energy. These disturbances can degrade or interrupt the function of electrical and electronic equipment. EMI can be generated by both natural and man-made sources, ranging from lightning strikes and solar activity to switching power supplies, electric motors, and digital circuits.
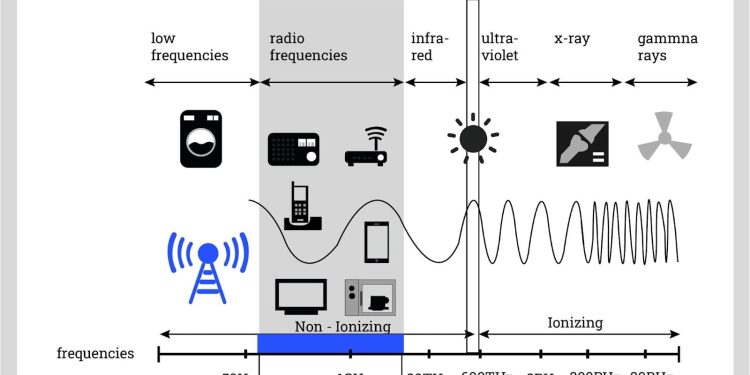
Radio frequency interference (RFI) is a subset of EMI that specifically occurs within the radio frequency (RF) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. While the full EMI spectrum extends from extremely low frequencies (ELF) below 3 Hz to microwave frequencies beyond 300 GHz, RFI typically refers to interference in the range from about 10 kHz to 100 GHz. In practice, most engineers associate RFI with disturbances that affect wireless communications, broadcast systems, and RF-sensitive devices.
Differences in Shielding Materials
Because RFI is a narrower category within EMI, the shielding materials used for each can be similar in construction but differ in their design focus and performance characteristics.
Frequency Range Considerations
EMI shielding materials must be effective across a very wide range of frequencies, from low-frequency magnetic fields to high-frequency electromagnetic waves. Shielding for low frequencies often relies on materials with high magnetic permeability, such as mu-metal, which can redirect magnetic fields.
RFI shielding materials, by contrast, are optimized for higher-frequency ranges. At these frequencies, conductive materials such as copper, aluminum, or silver-filled elastomers reflect and absorb RF energy. Mesh screens and conductive coatings are also common in RFI applications, where blocking wireless signals is the primary goal.
Material Comparison
EMI shielding materials may include laminates, foils, conductive plastics, or coated fabrics that address both electric and magnetic components of interference. They often need to balance mechanical strength, thermal performance, and corrosion resistance.
RFI shielding materials are generally more conductive and less dependent on magnetic permeability. For example, thin conductive gaskets, metallic meshes, or conductive paints are often sufficient to block high-frequency RF radiation.
Applications
EMI shielding is critical in environments with mixed electrical systems, such as aerospace and defense platforms, medical imaging equipment, and industrial control systems. Here, both low- and high-frequency interference can disrupt operations.
RFI shielding is more often discussed in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and wireless systems, where the concern is preventing signal leakage or blocking external RF noise that interferes with receivers.
Practical Overlap
Despite their differences, most modern shielding materials are marketed as EMI/RFI solutions because many applications require protection across a broad spectrum. Engineers typically consider regulatory standards, such as FCC, CISPR, or MIL-STD requirements, to determine the shielding effectiveness needed at specific frequencies.
Summary
The key difference between RFI and EMI shielding materials lies in their target frequency ranges and the material properties required to achieve effective attenuation. EMI shielding encompasses the entire electromagnetic spectrum and often requires specialized materials to handle both electric and magnetic fields. RFI shielding, as a subset, focuses on higher frequencies and relies heavily on conductivity to block or attenuate radio waves. For engineers, understanding this distinction ensures the correct choice of materials, preventing costly failures in performance and compliance.
The table below summarizes the differences between RFI shielding materials and EMI shielding materials.
| Aspect | EMI Shielding Materials | RFI Shielding Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Block or attenuate unwanted electromagnetic interference across a wide frequency spectrum | Block or attenuate radio frequency interference (a subset of EMI) in the RF spectrum |
| Frequency Range | Very broad: from ELF (<3 Hz) up to microwave (>300 GHz) | Narrower: typically 10 kHz – 100 GHz |
| Main Concern | Both low-frequency magnetic fields and high-frequency electromagnetic waves | Primarily high-frequency radio waves that affect communications and wireless systems |
| Material Properties | High conductivity and/or high magnetic permeability (e.g., mu-metal, conductive foils, laminates) | High conductivity; magnetic permeability less critical (e.g., copper, aluminum, conductive gaskets, meshes) |
| Examples of Materials | Mu-metal, conductive plastics, aluminum foils, nickel-coated fabrics, shielded enclosures | Copper mesh, silver-filled elastomers, conductive paints, RF shielding films |
| Applications | Aerospace, defense, medical imaging, industrial control, automotive electronics | Consumer electronics, wireless devices, telecommunications, RF test chambers |
| Shielding Mechanism | Combination of reflection, absorption, and magnetic field redirection | Primarily reflection and absorption of RF signals |
| Regulatory Standards | FCC, CISPR, MIL-STD, IEC standards depending on industry | FCC Part 15, CISPR 22, ITU-T, telecom-specific standards |