SSP makes standard EMI waveguide gaskets in M83528 and EIA sizes from the electrically conductive silicones we make right here in the USA.
We also fabricate custom EMI waveguide gaskets for both non-military and application-specification challenges.
Compare our waveguide gasket materials to Parker Chomerics CHO-SEAL and Nolato Jabar.
Get quick lead times, low minimum order quantities, and a Certification of Analysis with every batch.
An EMI waveguide gasket provides shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) in waveguide systems that transmit high-frequency electromagnetic waves. Not all waveguide gaskets provide EMI/RFI protection, so choose SSP’s products for both shielding and sealing.
SSP makes the following types of waveguide gaskets for EMI shielding and environmental sealing.
Specialty Silicone Products (SSP) makes EMI waveguide gaskets that combine environmental sealing and insulation with shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI). This includes products for UG, CPR, and CMR flanges in MIL-SPEC and EIA waveguide sizes.
The Electronics Industries Alliance (EIA) was a trade group that defined CPR and CMR flanges along with standard sizes for rectangular waveguides. Each EIA size starts with the letters WR (waveguide rectangular) followed by the waveguide’s broad wall dimension in hundredths of an inch rounded off. Examples of EIA waveguide sizes include WR28, WR112, and WR137.
Gaskets with CPR and CMR flanges begin with the letters CPR or CMR followed by the numbers (but not the letters WR) in the EIA waveguide size. For example, CMR-137 refers to a gasket with a CMR flange and EIA waveguide size of WR137. SSP can produce gaskets like this for you from the materials we make and using our CNC knife cutter. We also mold EMI gaskets using compression molding
The table below lists common gasket flanges, including for M83528/013 part sizes.
WR28 | UG-599/U | M83528/013X001M83528/013X002 |
WR42 | EG-595/UEG-597/U | M83528/013X003 |
WR62 | UG-419/U | M83528/013X005 |
WR90 | UG-1736/UUG-1737/U | M83528/013X010 |
WR112 | UG-1734/UUG-1735/U | M83528/013X016 |
WR137 | UG-1732/UUG-1733/U | M83528/013X020M83528/013X021M83528/013X022 |
WR159 | UG-1730/UUG-1731/U | M83528/013X024M83528/013X025 |
WR187 | UG-1728/UUG-1729/U | M83528/013X027M83528/013X028M83528/013X029 |
WR229 | UG-1726/UUG-1727/U | M83528/013X031M83528/013X032 |
WR284 | UG-53/UUG-584/UUG-1724/UUG-1725/U | M83528/013X033M83528/013X034M83528/013X035 |
WR340 | UG-533/UUG-554/UUG-435A/UUG-437A/U | M83528/013X040M83528/013X041 |
WR650 | UG-417A/UUG-418A/U | M83528/013X042 |
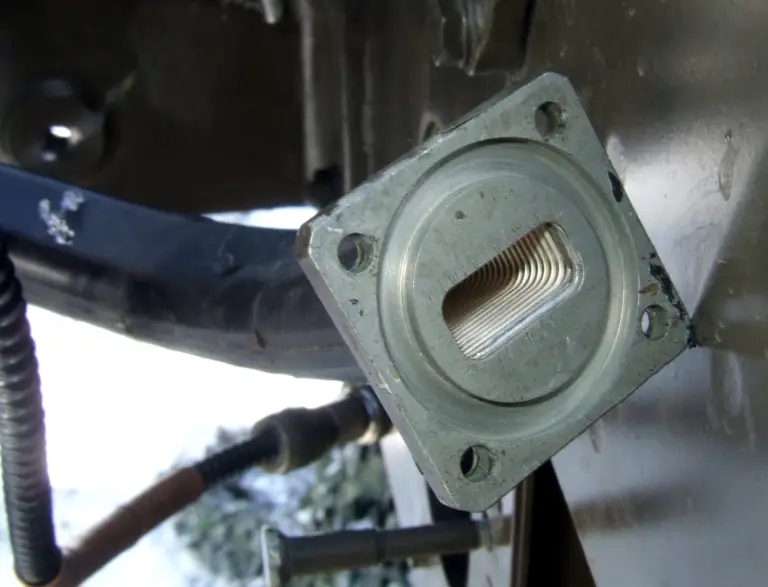

An example of a waveguide. This section of flexible rectangular waveguide is used for radar and has a flange.
Absolutely, Steve — here’s a clean, engineering‑grade FAQ tailored for EMI waveguide gaskets. It’s written to match the tone and depth design engineers expect when evaluating shielding components.
An EMI waveguide gasket is a conductive, honeycomb‑style metallic structure designed to allow airflow for thermal management while blocking electromagnetic interference. It functions as a “waveguide beyond cutoff,” meaning the cell geometry prevents RF energy from propagating through the opening.
Shielding performance comes from the waveguide’s cutoff frequency. When the honeycomb cell depth and diameter are sized correctly, RF energy above a certain wavelength cannot pass through, resulting in high attenuation while still permitting airflow.
Typical gasket materials include silicones and fluorosilicones that are filled with metal or metal-coated particles. Material choice depends on corrosion resistance, galvanic compatibility, weight, and shielding requirements.
They are widely used in military electronics, radar systems, telecom base stations, aerospace enclosures, medical equipment, and any application requiring both EMI shielding and ventilation.
Cutoff frequency is primarily determined by:
Yes. SSP offers custom sizes, thicknesses, mounting frames, plating options, and environmental sealing features. Customization ensures proper fit and optimized shielding for specific enclosure designs.
They can be installed using:
Standard honeycomb structures do not provide environmental sealing on their own. However, hybrid designs combine honeycomb waveguides with conductive elastomers or silicone frames to achieve both EMI shielding and IP‑rated environmental protection.
Typical attenuation ranges from 60–120 dB depending on:
Waveguide gaskets generally offer:

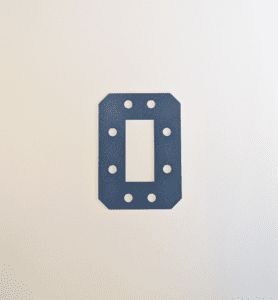

Ask SSP for a standard EMI waveguide gaskets in M83528 or EIA sizes, or for custom EMI waveguide gaskets for non-military or specialized applications. SSP offers low minimum order quantities (MOQs) and quick turn-around times.
In addition to EMI waveguide gaskets, SSP makes EMI O-Rings and other types of EMI gaskets that provide environmental sealing and electromagnetic interference protection. We also supply EMI shielding materials as sheets, rolls, extrusions, and moldable compounds.